Side-Effects Of Peripheral Neuropathy & Diabetic Neuropathy & Their Treatments!
What are the Complications & Symptoms and long term side effects of Peripheral Neuropathy & Diabetic Neuropathy?
Most of the time a peripheral neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy patient thinks that only feeling “pins and needles” or tingling or nerve pain in their feet and legs are the symptoms, complications, and side effects of peripheral neuropathy.
Maybe you feel like you’re wearing socks or gloves when you aren’t. Your feet may be very sensitive to touch—even a bed sheet can hurt. You think only these are all symptoms of peripheral nerve damage and complications associated with your neuropathy.
Yes, in the beginning, peripheral nerve damage affects your hands, feet, legs, and arms, and causes foot pain and leg pain. Numbness, alterations in sensations, and balance problems are the most common type of nerve damage symptoms for people with neuropathy. It generally starts in the feet, usually in both feet at once.
If you’re experiencing any of the above-mentioned symptoms, it’s important to seek effective treatment at the earliest. You may be at greater risk of developing side effects of peripheral neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy.
If you’ve been confirmed with peripheral neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy, don’t wait for the pain to worsen; immediately, start eating a balanced diet and begin natural remedies such as herbal and alternative therapy, as well as exercises (mentioned at the end of this page), right away.
But over time, untreated peripheral neuropathy may involve your body’s autonomic nerves, which can affect other organs.
Autonomic nerves automatically (involuntarily) regulate our various vital body processes. Autonomic neuropathy or autonomic dysfunction is a type of peripheral neuropathy, a disorder in which peripheral nerves are damaged throughout the body.
In autonomic neuropathies, there is much more damage to the autonomic nerves than to the somatic nerves.
Following are the Symptoms & Side effects of Peripheral Autonomic Neuropathy, Idiopathic Autonomic Neuropathy, and Diabetic Autonomic Neuropathy:
The symptoms of autonomic neuropathy depend on which of your body’s nerves and functions are affected. Autonomic neuropathy or dysautonomia is damage to nerves that control your internal organs.
Autonomic neuropathy or autonomic dysfunction is a collection of symptoms that arise when the nerves that control vital bodily activities are damaged. The nerves that supply the vital internal organs, such as the blood vessels, stomach, intestine, liver, kidneys, bladder, sex organs, lungs, pupils, heart, perspiration, salivary, and digestive glands, are affected by autonomic neuropathy.
Some nerve-related problems do not interfere with daily life. Others get worse quickly and may lead to long-term, severe symptoms and concerns.
Your outlook may be excellent when a medical condition can be found and treated.
№ 1. You may have muscle weakness: This is a common side effect of peripheral neuropathy. To help that, you may need physiotherapy to learn exercises to improve your muscle strength.
Physical therapy and exercises will be beneficial in maintaining strength, mobility, and function regardless of the underlying cause of peripheral neuropathy.
You may also need to wear splints to support weak ankles or use walking aids to help you get around.
№ 2. Vision-Related problems: Autonomic nerves control constriction of the pupil. Autonomic neuropathy or autonomic dysfunction also can affect the pupils of the eyes, causing the eyes to adapt slowly to changing light.
This makes it difficult to see when driving at night or when a light is switched on in a dark room. Change location slowly and wear good sunglasses.
№ 3. Cardiovascular system-related problems: Autonomic nerves control heart rate and blood pressure.
If these nerves are damaged, the blood pressure may drop sharply after you sit or stand, causing a feeling of lightheadedness.
Heart rate may remain high or too low instead of fluctuating with body functions and exercise.
№ 4. Dryness in Mouth (Xerostomia):
Oral dryness (xerostomia) and peripheral neuropathy (PN) are two common diabetes-related problems, and there is some definitive link between the two.
Multiple oral health problems emerge with diabetic neuropathy. In many cases, these debilitating complications impact the oral health of neuropathy patients and their ability to eat, talk, smile, or even feel comfortable.
One of them is dryness in the mouth, medically called Xerostomia. Xerostomia is a symptom, not a disease entity, and can be temporary, reversible, or permanent.
It occurs when salivary glands in your mouth don’t produce enough saliva.
This condition causes a parched, or dry, feeling in your mouth. It can also cause other symptoms, such as bad breath, a dry throat, and cracked lips.
A dry mouth can aggravate the side effects of diabetes, which will then increase glucose levels, wreaking havoc on the body.
A dry mouth is not only a symptom of high blood sugar, but it can also be the cause of it.
Dryness in the mouth, especially as a diabetic, can lead to rampant tooth decay, which means blood sugar increases as the body tries, and fails, to fight infection.
№ 5. Muscle Spasms or Muscle Cramps:
A muscle spasm or muscle cramp is a sudden and involuntary contraction of one or more of your muscles. During cramping, your muscles suddenly contract (shorten), causing leg cramps and pain. This is also known as cramping; you cannot control the affected muscle. The cramping can last from a few seconds to 10 minutes. When the cramping passes, you can maintain the affected muscle again.
A lot of neuropathy patients ask the following questions:
Does nerve damage cause muscle spasms?
Can neuropathy cause leg cramp?
Can neuropathy cause cramping?
Does peripheral neuropathy cause cramping?
Does diabetic neuropathy cause muscle cramps?
Can diabetic neuropathy cause muscle twitching?
Can nerve disease cause foot and leg cramps?
Foot and leg cramps: Is nerve disease to blame?
Yes, the answer to all of the above is the same. Muscle spasms, muscle cramps, leg cramps, and foot cramping can occur due to certain types of nerve disease, such as peripheral neuropathy and diabetic neuropathy.
What Causes Muscle Spasms? Your nerves are damaged when you have neuropathy, which is common in people with diabetes. As a result, proper messages from your muscles to your brain are not sent. As a result, your muscles may fire up and start cramping at inopportune times.
Major risk factors for muscle spasms and leg cramps may include neuropathy, lack of specific minerals and vitamins in your body, poor physical condition, dehydration, and muscle fatigue. Muscle tissue relies, in part, on a range of minerals, electrolytes, and other chemicals to contract and relax.
Cramping is an insufficiently acknowledged common neurological but uncomfortable symptom that affects a significant proportion of individuals suffering from peripheral and diabetic neuropathy. But muscle spasms are more common in patients with diabetic neuropathy as a direct result of long-term high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia).
Night leg cramps, also known as nocturnal leg cramps, are excruciating, involuntary contractions or spasms of muscles in your legs that tend to happen while you are sleeping. Night leg cramps tend to affect your calf muscles but can also impair your feet or thighs. The pain is eased by trying to stretch the contracted muscle vigorously.
Muscle cramps are characterized by the involuntary, painful, and confined contraction of an entire muscle group, a single muscle, or a group of muscle fibers. In peripheral neuropathy and diabetic neuropathy patients, the cramping can last anywhere from minutes to a few seconds.
Muscle spasms are a common complaint that is thought to be caused by spontaneous motor nerve terminal discharges. In addition, Polyneuropathy is a common cause of muscle cramps.
The presence of neuropathy, or hyperexcitability of the peripheral nerve, is linked to the onset of cramping in people with diabetes. When compared to type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes has a lower percentage of cramps (around 60%) compared to type 2 diabetes (about 80 %). Nephropathy is another cause of cramping in people with type 2 diabetes. Another possible cause of muscle spasms is a change in peripheral microcirculation, which can ultimately lead to ischemia and cramping.
Ischemia is a condition in which the blood flow (and thus oxygen) is restricted or reduced in a part of the body.
Peripheral neuropathy and diabetic neuropathy can cause leg pain and leg cramps, but there are ways to relieve them. In addition, leg pain and cramping can be managed to help prevent the condition from worsening and to improve your overall quality of life!
You can stop muscle spasms and leg cramps in their tracks and prevent cramping from returning with a clinically researched formula. Expertly formulated based on clinical studies with the efficiency of specific minerals and vitamins can combat your muscle spasms and leg cramps.
Longing For Muscle Spasm & Leg Cramps Relief? Discover how to stop cramps in their tracks and prevent them from returning with a clinically researched formula!
№ 7. Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a globally prevalent disease with systemic consequences.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Definition: Obstructive sleep apnea is a persistent disorder in which the upper airway repeatedly collapses during sleep. Its impact on nocturnal sleep quality and the resulting weariness and sleepiness during the day is well known.
Obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea are the two most common kinds of sleep apnea:
When the mechanics of your breathing get obstructed, you develop obstructive sleep apnea or OSA. Central sleep apnea, or CSA, occurs when your brain fails to send the proper signals to your muscles. As a result, you may briefly stop breathing or breathe so weakly that you may not get enough oxygen.
People with obstructive sleep apnea subconsciously awaken many times a night — even dozens of times an hour — because their airways close, disrupting their breathing.
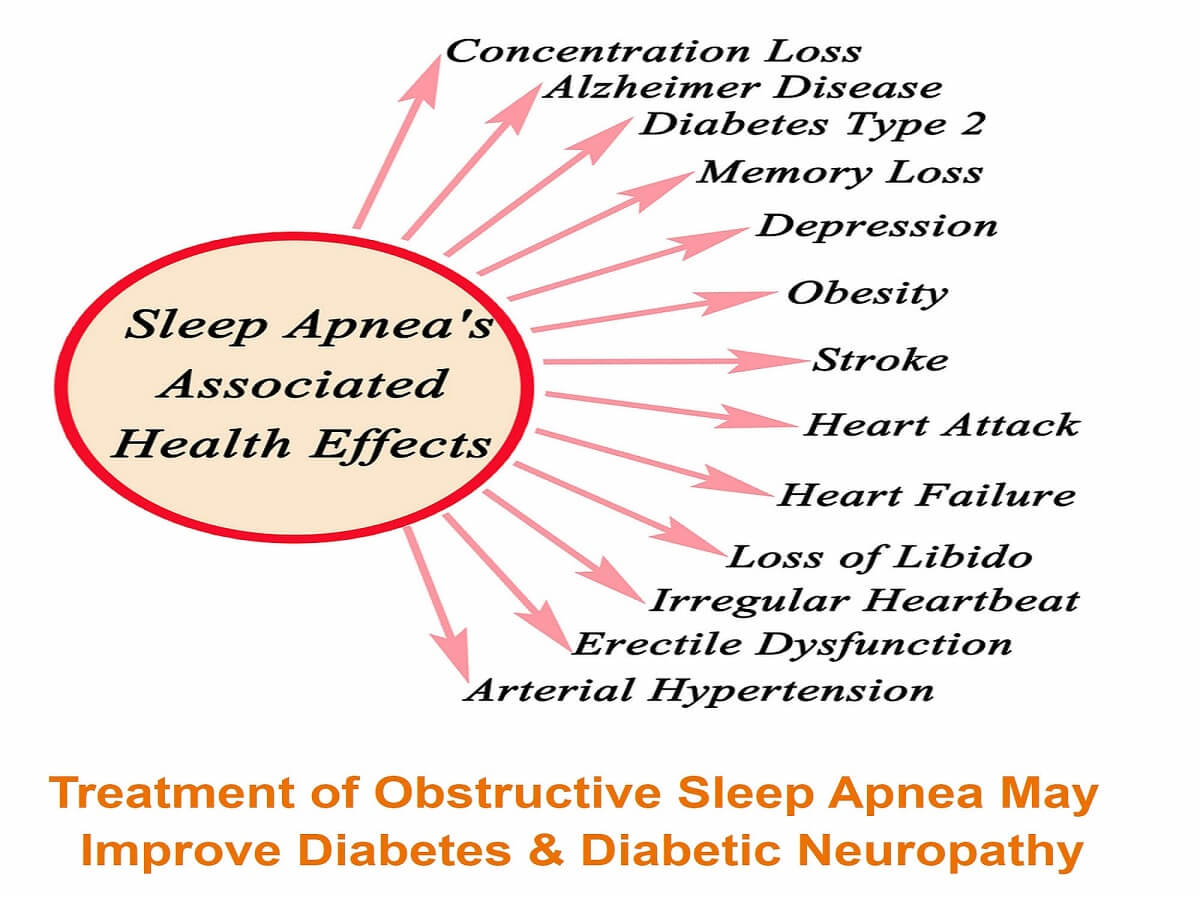
Increasingly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common sleep-related breathing issue that can lead to various life-threatening conditions. Obstructive sleep apnea affects multiple organ systems on a systemic level. Long-term health effects of untreated obstructive sleep apnea or OSA include hypertension, heart disease, diabetes, depression, metabolic problems, and stroke.
Untreated obstructive sleep apnea is now linked to an elevated risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, according to a significant amount of evidence.
As per the latest scientific studies and BMC journals, severe obstructive sleep apnea not only causes insufficient sleep ( a sleep disorder) but can also lead to various severe health and medical ailments such as nerve damage, neuropathy, loss of libido, erectile dysfunction, obesity, stroke, heart failure, diabetes mellitus, depression, Alzheimer’s disease, etc.
People who have diabetes often have poor sleep habits, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Causes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
In adults, the most common cause of obstructive sleep apnea is excess weight and obesity, which is associated with the mouth and soft throat tissue. During sleep, when throat and tongue muscles are more relaxed, this soft tissue can cause the airway to become blocked.
Other possible causes or risk factors for OSA include narrow throat, round head, hypothyroidism, medical conditions that congest upper airways, smoking, alcohol or drug abuse, etc.
Individuals with diabetic peripheral neuropathy with type 2 diabetes & obesity have a greater chance of developing accompanying sleep disorders, the most common being obstructive sleep apnea.
An ever-growing number of research studies have shown that obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is associated with insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and type 2 diabetes. In addition, OSA is associated with many of the pathophysiological deficits that are found in diabetes.
According to a new scientific study, obstructive sleep apnea is associated with nerve damage in people with type 2 diabetes.
Can Obstructive Sleep Apnea cause peripheral neuropathy?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is suggested to be associated with peripheral nerve damage and peripheral neuropathy.
Sleep apnea patients have peripheral nerve dysfunction whose severity is partly related to the level of nocturnal hypoxemia (Temporary drop in oxygen saturation during sleep).
Studies have shown that obstructive sleep apnea causes a stress response that clamps down on blood vessels of the distant extremities. Thus, while the blood supply to nerves is obstructed, it leads to the deficiency of oxygen and nutrients in peripheral nerves and organs that may cause nerve damage, nerve pain, and neuropathy.
Based on research data by NCBI, USA, it seems reasonable to conclude that obstructive sleep apnea could play a crucial role in the development or progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Effective Obstructive Sleep Apnea Treatment:
The recommended treatment for obstructive sleep apnea is to use a CPAP device. CPAP stands for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. The CPAP machine is a simple device that uses pressure to keep your airways open.
Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea by CPAP machine May Improve Diabetes & Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.
CPAP machine is the most consistently compelling and widely used method of treating obstructive sleep apnea. A continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine is one of the most successful and first-line treatments for sleep apnea or OSA in adults.
Researchers have found that treating obstructive sleep apnea with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices not only helped people sleep better but also helped with diabetes and diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
CPAP improves their blood sugar (glucose) levels by lowering insulin resistance, which can reduce the risk of complications from diabetic peripheral neuropathy and diabetes.
By improving sleep, CPAP may improve hormone levels.
Therefore, treating your obstructive sleep apnea problem will help you a long way to reduce the diabetic nerve pain, numbness, and tingling in your feet, legs, hands, and arms due to your diabetic peripheral neuropathy.
Scientifically proven effective therapy of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) will also help to stop further damage to nerves, tissues, and major body organs like the heart, kidney, sex organs, brain, etc.
№ 8. Constipation-: Side Effects of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral Neuropathy And Diabetic Neuropathy Can Cause Nerve Damage In Different Parts Of The Body, Including The Digestive Tract.
Diabetes-related nerve damage may affect the autonomic nerves, which control the movement of food through our digestive tract. Constipation is a significant side effect of neuropathy.
When this occurs, a person’s bowels cannot process solid waste as effectively. In addition, injured autonomic nerves can affect your digestion, bowel movements, and bladder emptying, and as a result, a person may become constipated.
It is advised that people with diabetes must eat a well-balanced diet to prevent blood sugar spikes and maintain a healthy weight. A healthful, varied diet that contains plenty of fiber can also help people with this condition prevent constipation.
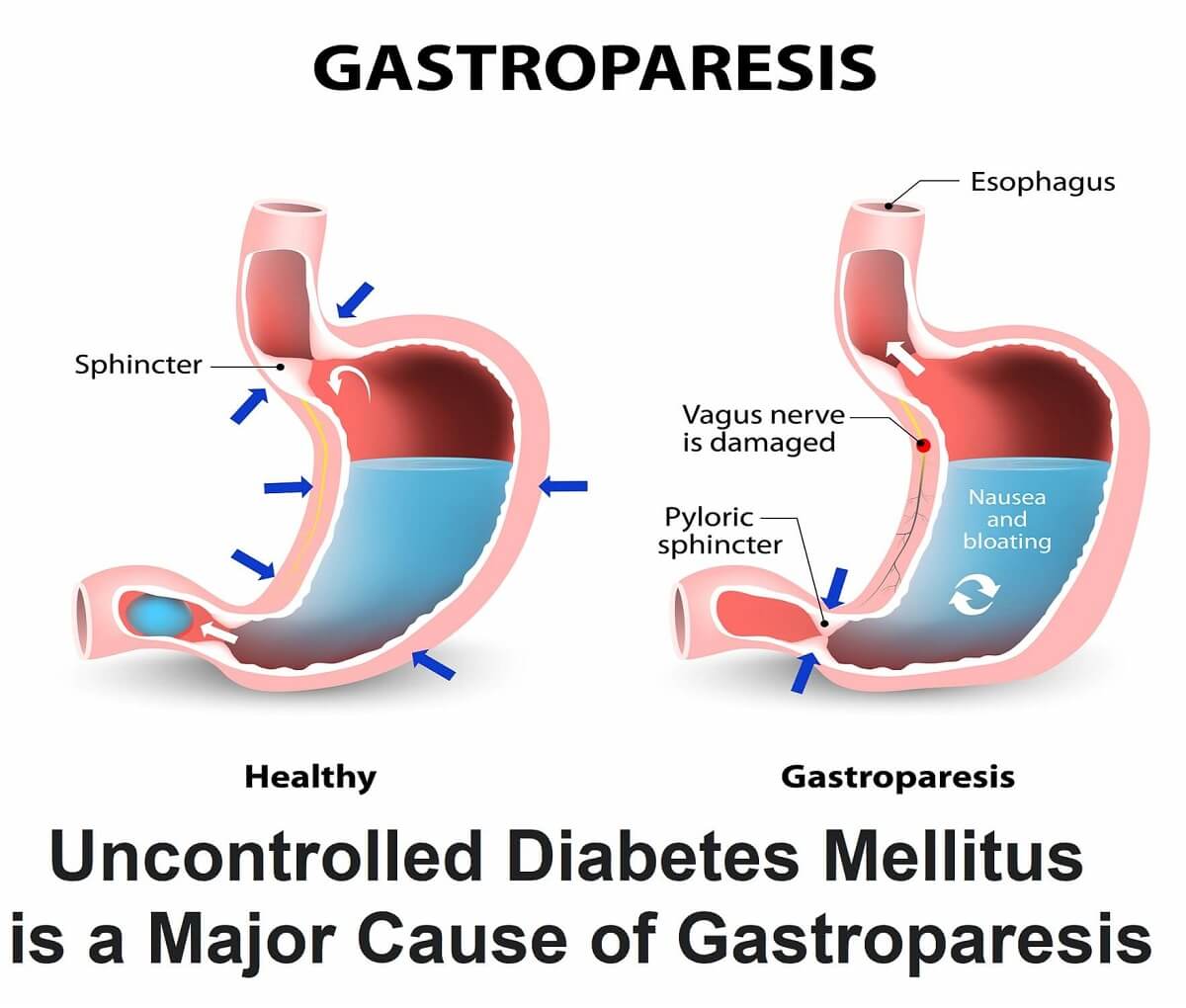
№ 9. Gastroparesis: Side Effects of Peripheral Neuropathy
What is Gastroparesis:
Gastroparesis, Also Called Delayed Gastric Emptying, Is A Medical Disorder Consisting Of Weak Muscular Contractions (Peristalsis) Of The Stomach, Resulting In Food And Liquid Remaining In The Stomach For A Prolonged Period.
When you have gastroparesis, your stomach muscles work poorly or not at all, and your stomach takes too long to empty its contents. Gastroparesis can delay digestion, which can lead to various symptoms and complications.
Symptoms of Gastroparesis: Symptoms o gastroparesis include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, feeling full soon after beginning to eat (early satiety), abdominal bloating, heartburn, etc.
What Causes Gastroparesis?
Even with medical tests, doctors are unable to identify the underlying cause of gastroparesis in the majority of cases. Idiopathic gastroparesis refers to gastroparesis that has no known cause.
Diabetic Gastroparesis
The most common known underlying cause of gastroparesis is uncontrolled diabetes. Diabetes can harm nerves, such as the vagus nerve, as well as nerves and special cells in the stomach wall known as pacemaker cells. The stomach and small intestine muscles are managed by the vagus nerve.
The muscles of the stomach and small intestine do not function normally if the vagus nerve is damaged or ceases to function. Food passage through the digestive tract is then slowed or stopped. Similarly, if the stomach nerves are damaged or do not function normally, the stomach does not empty.
What Can You Do to Avoid Gastroparesis?
Gastroparesis with no known cause, known as idiopathic gastroparesis, cannot be avoided.
If you have diabetes, you can prevent or delay nerve damage that can lead to gastroparesis by keeping your blood glucose levels within the target range recommended by your doctor. Meal planning, physical activity, and, if needed, medications can all help you keep your blood glucose levels within the target range.
Are you suffering from any of the above-mentioned side effects of peripheral neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy and have any of the above-noted complications also?
Do not delay. When a medical condition can be found and treated, your outlook may be excellent.
The good news is that you can treat these health complications and side effects of peripheral neuropathy by taking good care of yourself and treating them as soon as possible.
You can naturally stop or manage your health problems caused by side effects of peripheral neuropathy,
diabetic neuropathy, and autonomic neuropathy. You will eventually be able to cure and reverse it, with the help of medically proven and clinically tested natural treatments and alternative therapies.
The regeneration of injured nerves necessarily involves the use of a broad range of medical tactics, actions, and measures at the same time. Starting one or more of the scientifically proven and effective treatments for peripheral neuropathy and diabetic neuropathy listed below would be beneficial:
►Medically approved and time-tested safe and effective total herbal treatment to rejuvenate injured nerves and reverse peripheral neuropathy, idiopathic neuropathy, and diabetic neuropathy.
►All-powerful and natural homeopathy therapy to stop neuropathic pain, and eliminate peripheral neuropathy, idiopathic neuropathy, and diabetic neuropathy.
►The best and the most effective and scientifically proven natural treatment for neuropathy and nerve damage PEMF – Magnetic Therapy is an effective and medically proven nerve pain reliever to cure and reverse peripheral neuropathy, idiopathic neuropathy, and diabetic neuropathy.
And also try to add hypnotherapy as a form of complementary therapy and Alternative Pain Management program to produce additive or potentiated positive health effects.
These non-prescription remedies are cost-effective, drug-free, and have no negative side effects. Furthermore, these health disorders can be treated at home.
You should start the medically proven, time-tested most up-to-date evidence-based natural treatments for peripheral neuropathy or diabetic neuropathy, in combination with the above-mentioned treatments, for complications and side-effects of neuropathy, immediately.
Begin your treatment now and commit to continuing it each day. Challenge yourself to begin the journey to your new illness-free & Pain- Free Healthy Life!
15% Discount Code: TPN15 (for a limited time)
Get here the safest & most effective non-pharmaceutical scientifically formulated product by a board-certified Pain Specialist Doctor (MD) to reduce your nerve damage, nerve pain, & muscle
pain and stop, treat and ultimately reverse your & peripheral neuropathy & diabetic neuropathy!!

Affiliate Disclosure “If you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission, no worries though, you’ll still pay the standard amount so there’s no cost on your part. However, please know this does not impact our reviews and product information. We try to keep things fair and balanced to help you make the best choice for your needs. This keeps it 100% reader-supported and free of advertisements or sponsorships. Thanks for your support!”
Medical Disclaimer:
All content and media on this Website are created and published
online for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute
for professional medical advice and should not be relied on as health or
personal advice.
Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified
health professional with any questions you may have regarding your health or a
medical condition. Never disregard the advice of a medical professional, or
delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this Website.